Growth Chamber
| Container.................. | 10-cm plastic pots or flats |
| Medium.................... | Potting soil mix |
| Temp/Light................ | 23°C; 16+ hour daylength |
| No. of Plants............. | 50 per replication |
| No. of Reps............... | 4 minimum |
| Other........................ | Control insects and fertilize as necessary |
| INOCULUM CULTURE | |
| Source .................... | Infected stem tissue |
| Storage..................... | Soil or silica gel (7) |
| Temperature.............. | 4°C |
| Storage Life .............. | Up to several years |
| INOCULATION PROCEDURE | |
| Age of Plant.............. | 7-14 days (take stand counts at 7 days) |
| Type of Inoc.............. | Spore suspension with 2 drops Tween per L distilled water, taken from 7 day old cultures incubated at 23°C on half strength oatmeal agar |
| Concentration ........... | 2X106 spores per mL |
| Method .................... | Spray to runoff, approx. 3 mL per pot or 5 to 10 mL per flat; place in mist chamber to maintain 100% R.H. for 48 hours 23°C |
| INCUBATION | |
| Location.................... | Growth room or greenhouse at 23°C |
| Age at Rating ........... | 10 to 14 days after inoculation |
|
RATING Resistance is assessed as a percent of the stand surviving 10 to 14 days after inoculation. | |
| CHECK CULTIVARS (Race 1) | |
| Approximate Expected Resistance (%) | Acceptable Range of Reaction (%) | |
| Resistant | ||
| Arc** | 65-70 | 45-80 |
| Saranac AR** | 45 | 40-60 |
| Susceptible | ||
| Saranac** | 1 | 0-5 |
| Values for resistant
standards are percent survivors.
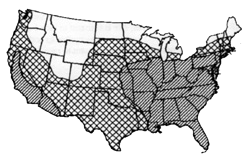
DISTRIBUTION AND SEVERITY OF Anthracnose, Collelotrichum trifolii Bain & Essary (Click on the map for a larger version; see the key here). SOURCE OF
INOCULUM
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||